Understand Ohms Law in 10 Minutes or Less! GreyMattersGlobal Academy

"Ohms Law" Poster for Sale by KiwiMrDee Ohms law, Electronics basics
Ohm's Law Learning Objectives. In this lesson you will see: the mathematical relationship between voltage, current and resistance call Ohm's Law. the Ohm's Law circle and use it to find the three forms of the formula examples using Ohm's Law to find voltage, current and resistance the linear mathematical relationship between voltage and.

Printable Ohms Law Wheel Printable Word Searches
What is Ohm's Law? Electrical, Fundamentals. Ohm's Law is a formula used to calculate the relationship between voltage, current and resistance in an electrical circuit. To students of electronics, Ohm's Law (E = IR) is as fundamentally important as Einstein's Relativity equation (E = mc²) is to physicists.
Electrical & Electronic Engineering Ohm's Law, Current Voltage
An object that has simple resistance is called a resistor, even if its resistance is small. The unit for resistance is an ohm and is given the symbol Ω (upper case Greek omega). Rearranging I = V / R gives R = V / I, and so the units of resistance are 1 ohm = 1 volt per ampere: 1 Ω = 1 V A. Figure 9.9. 1 shows the schematic for a simple.
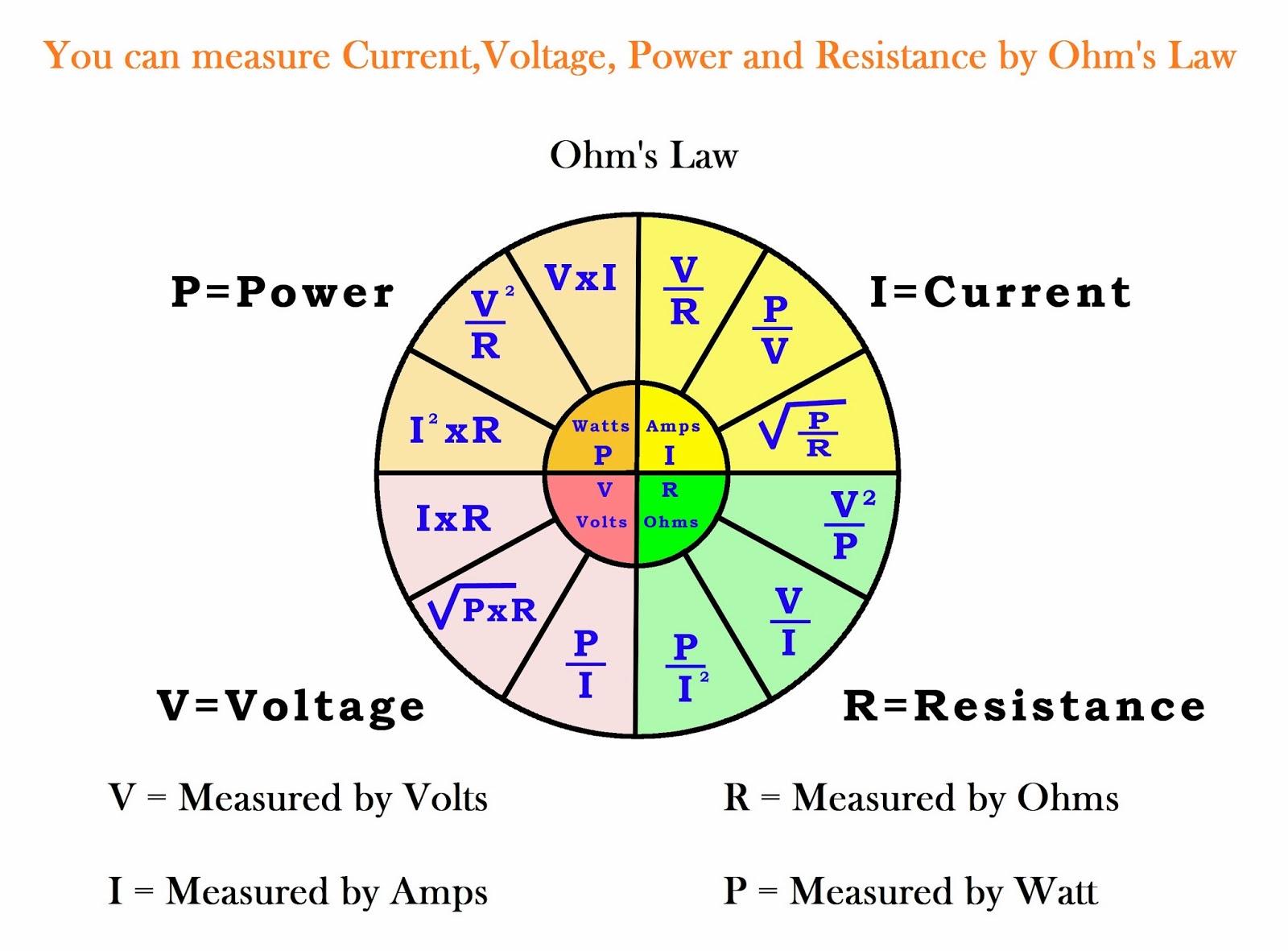
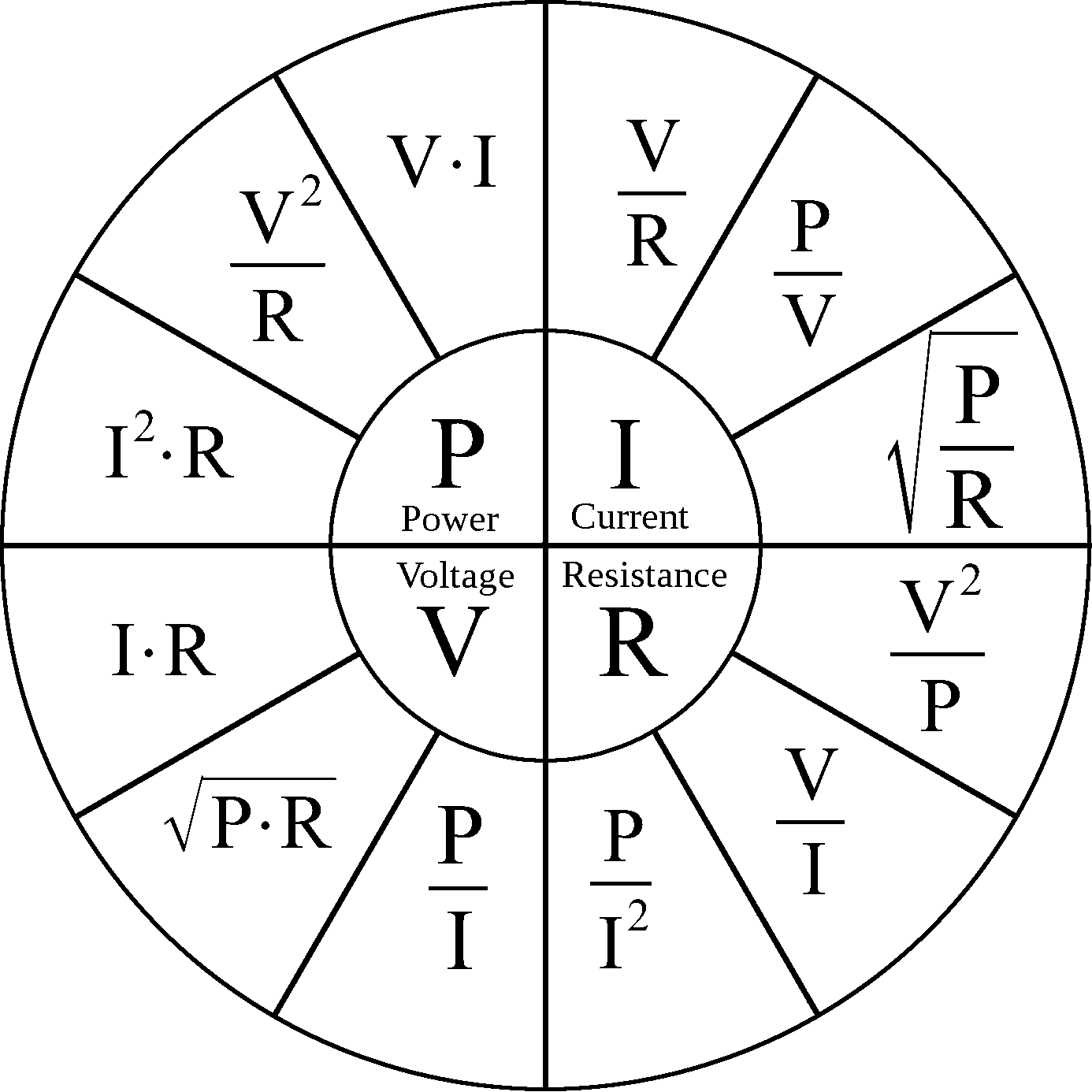
The Ohm's law and PIR wheel The Wheel and How To Use It
Ohm's Law. Ohm's law states that for some devices there is a relationship between electric potential difference, current, and resistance. The equation is: I = Δ V R. Where I is current, Δ V is electric potential difference, and R is resistance.
Exploring Ohm's Law. Off Grid Ham
Ohm's Law Formula. V = IR V = I R. In the formula for Ohm's Law, V V represents voltage measured in volts (V), I I is the current measured in amperes (A), and R R is the resistance measured in ohms (Ω). This formula is the cornerstone for analyzing and understanding electrical circuits, requiring two variables to solve.

Ohm's Law Circle Poster
The lightbulb filament violates Ohm's Law. Ohm's Law Statement: Ohm's law states that the voltage across a conductor is directly proportional to the current flowing through it, provided all physical conditions and temperature, remain constant. Ohm's Law Equation: V = IR, where V is the voltage across the conductor, I is the current.

Printable Ohms Law Wheel Printable Blank World
#accesstopower #OhmsLaw #AccessElectrichttps://accesstopower.comIn this video, we look at the 12 math equations on the Ohms Law Wheel and show you how you ca.

Ohm's Law Voltage, Current, and Resistance EE Calculator
where I is the current through the conductor, V is the voltage measured across the conductor and R is the resistance of the conductor. More specifically, Ohm's law states that the R in this relation is constant, independent of the current. If the resistance is not constant, the previous equation cannot be called Ohm's law, but it can still be used as a definition of static/DC resistance.

I think this is the best photo of the Ohm,s Law becouse it explains you
By putting the known values in the Ohm's law formula wheel: 24 volts / 6 ohms = 4 amps. Now you know the missing variable's value. You can use Ohm's law whenever you know two unit variables in the formula. Here's another example in which you have 200 volts and 20 amps: 200 volts / 20 amps = 10 ohms.
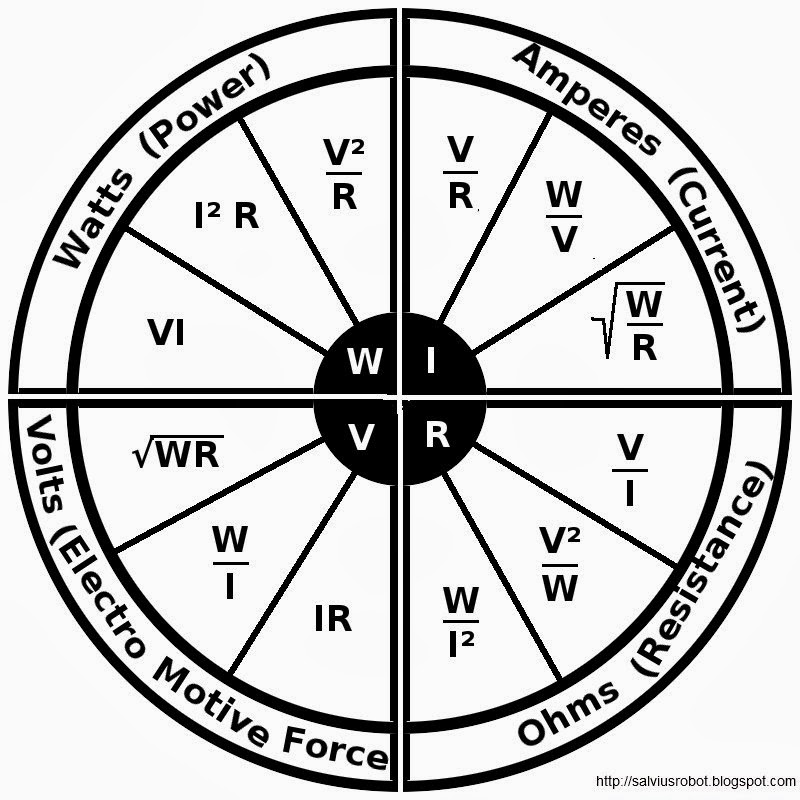
Ohm's Law Wheel Printable
Free Shipping on eBay! Shop for Ohms Law now
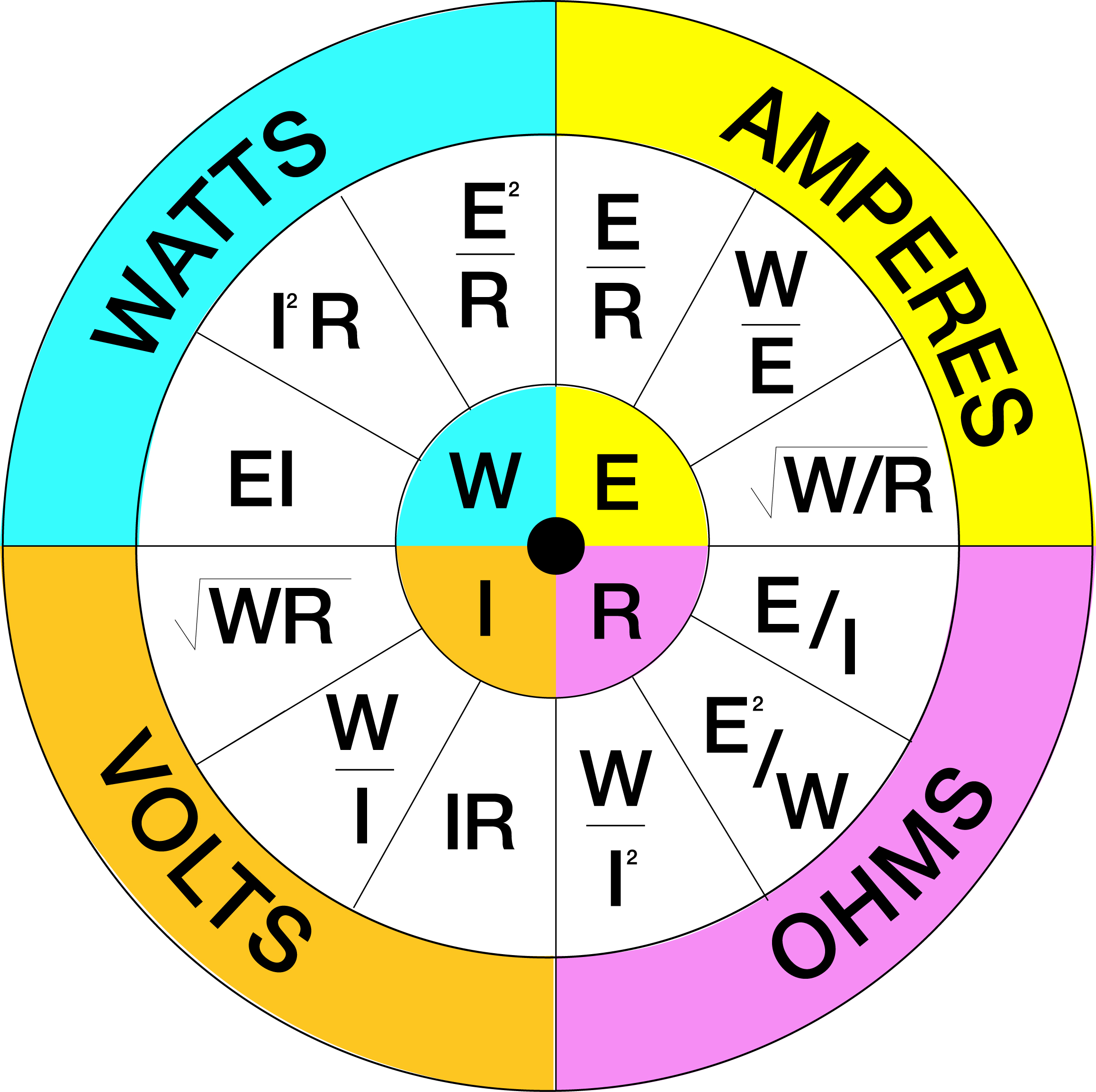
Dale Swanson Ohm's Circle
The current through the resistor and the voltage across the resistor are measured. A plot is made of the voltage versus the current, and the result is approximately linear. The slope of the line is the resistance, or the voltage divided by the current. This result is known as Ohm's law: V = IR (9.5.2) (9.5.2) V = I R.

Ohm’s Law Event Power your event power specialists
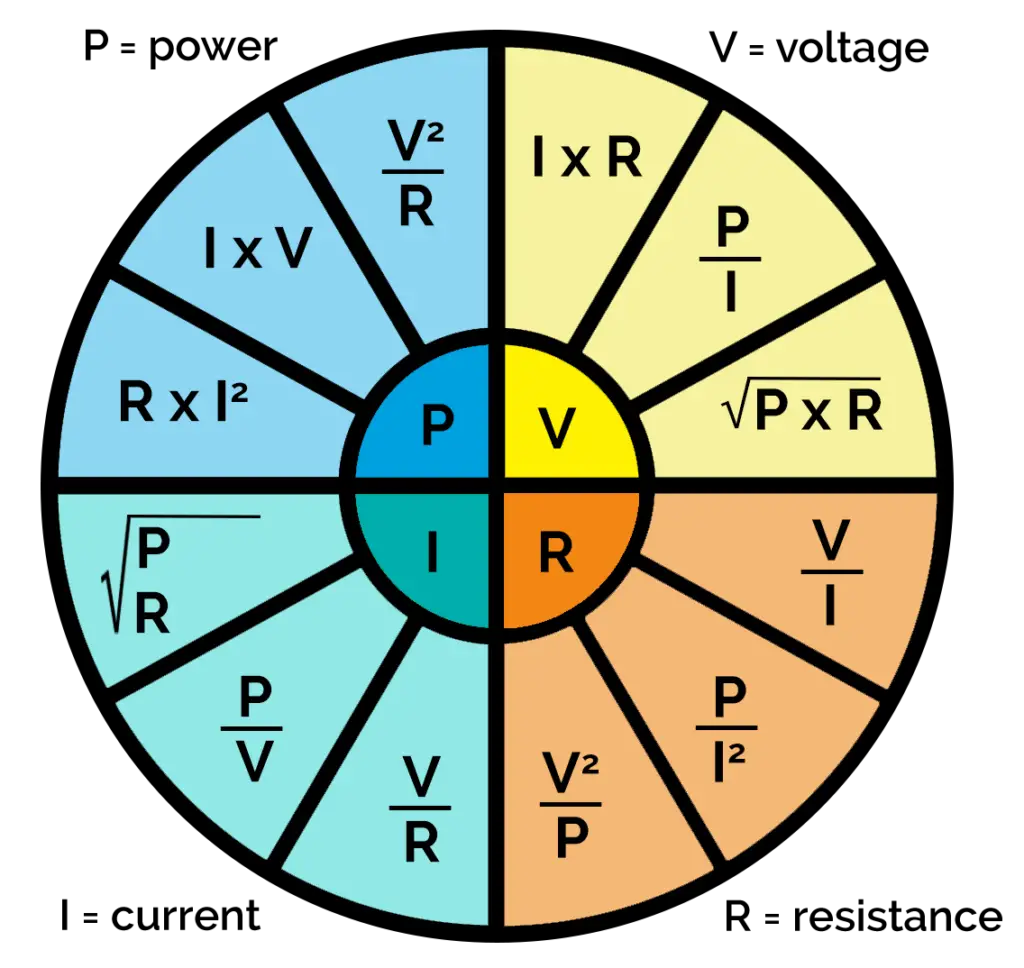
Ohm's Wheel is a collection of 12 different formulas which helps to calculate Voltage, Current, Power, and Resistance. Let's take a look at Ohm's wheel: We can use the wheel to extract 12 formulas (3 for each voltage, current, power, and resistance): V = IR. V = P/I. V = (P.R) 1/2. P = VI.

Understanding the Basics of Ohm's Law Electrician Apprentice Headquarters
20.12. This important relationship is known as Ohm's law. It can be viewed as a cause-and-effect relationship, with voltage the cause and current the effect. This is an empirical law like that for friction—an experimentally observed phenomenon. Such a linear relationship doesn't always occur.

Dale Swanson Ohm's Circle
Ohms Law Wheel. Ohm's law (named after the German physicist Georg Ohm) defines the relationship between Voltage, Current and Resistance. V = I x R. Where: V is the electrical potential (voltage), measured in volts (V), I is the current, measured in Amperes (Amps/A), and. R is the resistance, measured in Ohms (Ω). Joule's law states that:

A rendition of the ohms law circle chart. Size Large,3 inch (sheet of
This formula wheel is a combination of both Ohm's Law and the PIE formula. It looks more complicated but in reality, it's easy to use (you may need a calculator), and it works the same way as the previous charts. The formula wheel is divided into four sections, each section has three formulas . If you need to find volts then you would use.

Ohms Law Circle Diagram Electrical Formula Stok Vektör (Telifsiz
Ohm's law: The current flowing through any resistor is directly proportional to the voltage applied to its ends. Mathematically Ohm's Law is given by V = IR. Where. V = Voltage, I = Current, R = Resistance. Ohm's Law is widely used in Electrical Engineering for solving circuits.